The 6RD feature is an extension of the 6to4 feature. The 6RD
feature allows a service provider (SP) to provide a unicast IPv6 service
to customers over its IPv4 network by using encapsulation of IPv6 in
IPv4.
The main differences between 6RD and 6to4 tunneling are as follows:
-
6RD does not require addresses to have a 2002::/16 prefix; therefore,
the prefix can be from the SP’s own address block. This function allows
the 6RD operational domain to be within the SP network. From the
perspective of customer sites and the general IPv6 internet connected to
a 6RD-enabled SP network, the IPv6 service provided is equivalent to
native IPv6.
-
All 32 bits of the IPv4 destination need not be carried in the IPv6
payload header. The IPv4 destination is obtained from a combination of
bits in the payload header and information on the router. Furthermore,
the IPv4 address is not at a fixed location in the IPv6 header as it is
in 6to4.
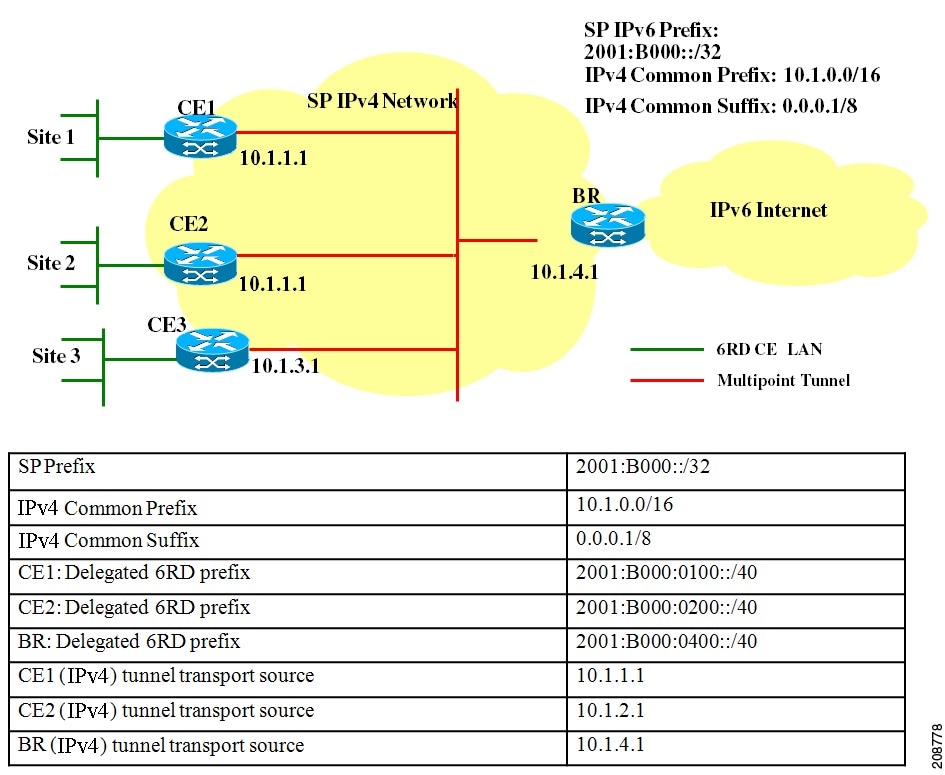
The 6RD SP prefix was selected by the SP for the IPv6 deployment
shown in the figure below. The 6RD delegated prefix is derived from the
SP prefix and the IPv4 address bits, and is used by the CE for hosts
within its site.
Figure 1. 6RD Deployment 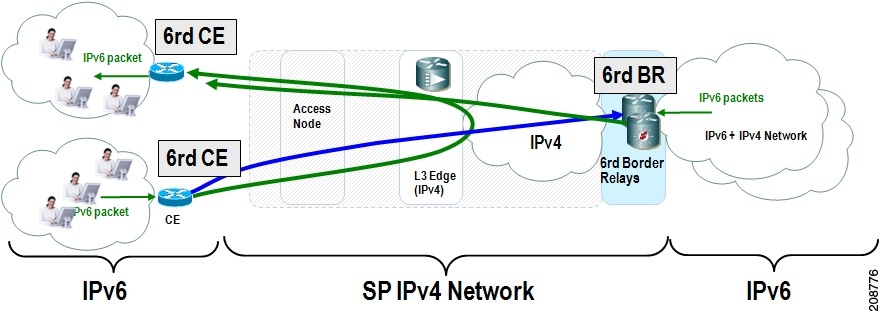
The figure below shows how 6RD prefix delegation works.
Figure 2. 6RD Prefix Delegation Explanation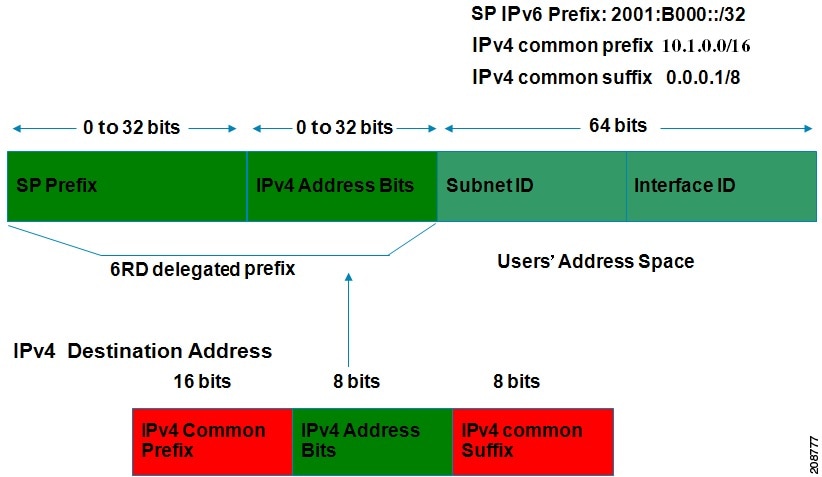
The figure below shows a 6RD prefix delegation topology.
Figure 3. 6RD Prefix Delegation and Explanation