Conclusion
Flex link is a Cisco solution which replaces STP in certain network topologies. It
works by detecting link down on a primary interface and then bringing up the backup
interface that has been defined as backup. It is most commonly implemented at the access
layer where the switch has dual uplinks to the distribution layer.
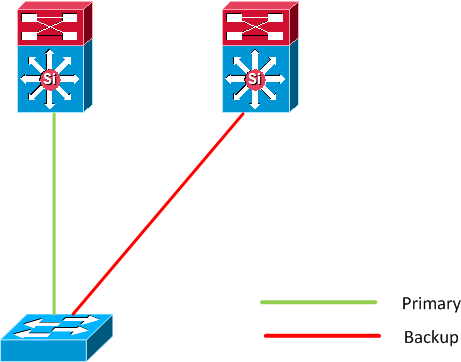
How does it work?
Under the primary interface the backup interface is defined with the switchport backup
interface command. This command can be applied to L2 links or portchannels. The backup
interface is kept in down state until the primary fails. Under normal conditions traffic
will flow through the primary interface so all dynamic MAC entries are learned via the
primary interface.
As soon as the primary interface goes down the backup interface is brought online.
These things happen when the primary fails:
- All dynamic MAC entries are moved to the backup interface
- Moves the backup link into a forwarding state
- Transmit dummy multicast frames to multicast destination 01:00:0c:cd:cd:cd
- The source of these frames are the sources learned by the switch on its local ports
transmitted and STP is disabled on the interfaces that are enabled for Flex link.
Bringing the backup interface up is very fast and should take less than a second. To send
out dummy multicast frames the MAC-address table move update feature needs to be enabled.
Preemption
Preemption is disabled by default. Enabling preemption means that the primary interface
will be brought into forwarding when it comes back. There is a preemption delay that can
be set to prevent flapping. Enable preemption if you have a primary interface of
higher bandwidth than the backup one.
Load balancing
Flex link can support load balancing. This means that one interface is primary for a set
of VLANs and backup for other VLANs and vice versa. Enable this if you need to use both
uplinks to support the amount of traffic exiting the switch.
Advantages of Flex links
What are the advantages of Flex link?
- Light weight, no BPDUs transmitted.
- Fast to converge
- The topology is deterministic and not subject to STP reconverging due to misconfig
There are always negative sides with every solution/protocol in networking. It’s always
a choice to make to make the right design.
- Relies on link down to detect failure
- Can’t detect unidirectional links
- Can’t detect wonky SFP or hardware failure not leading to link down
- Risk of loops in certain topologies
Risk of loops
So how could a loop be formed with Flex link? The first scenario is that someone
accidentally connects two access switches together.
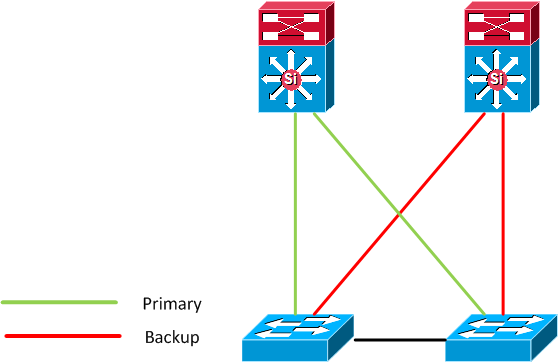
Because Flex link has no concept of STP if the link between the access switches is
brought into forwarding a loop has formed. This could be stopped by implementing BPDU
guard on all non uplink ports.
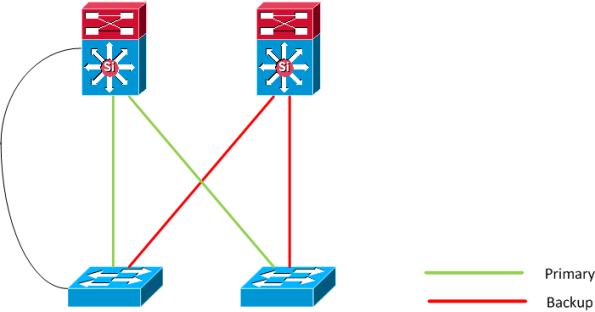
There could also be a situation where a link is added between the access and distribution
layer and because the Flex link does not consume/send BPDUs a loop could form.
Summary
Flex link is a STP replacement from Cisco that works by bringing up an backup interface
when the primary interface has gone link down. It is light weight and fast but relies
on links going physically down. It also has the risk of loops in certain topologies.
It’s a viable solution where STP is not wanted due to buying a L2 service from a
provider or such to not mix STP with the