Information About ICMP Unreachable Destination Counters
To configure the ICMP Unreachable Counters feature, you should understand the following concepts:
ICMP Overview
Originally created for the TCP/IP suite in RFC
792, the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) was designed to report
a small set of error conditions. ICMP also can report a wide variety of
error conditions, provide feedback and testing capabilities. It is a
valuable support tool because each message uses a common format and is
sent and received by using the same protocol rules.
ICMP enables IP to perform addressing, datagram
packaging, and routing by allowing encapsulated messages to be sent and
received between IP devices. These messages are encapsulated in IP
datagrams just like any other IP message. When the message is generated,
the original IP header is encapsulated in the ICMP message and these
two pieces are encapsulated within a new IP header to be returned as an
error report to the sending device.
ICMP messages are sent in several situations:
for example, when a datagram cannot reach its destination, when the
gateway does not have the buffering capacity to forward a datagram, and
when the gateway can direct the host to send traffic on a shorter route.
To avoid the infinite regress of messages about messages, no ICMP
messages are sent about ICMP messages.
ICMP does not make IP reliable or ensure the
delivery of datagrams or the return of a control message. Some datagrams
may be dropped without any report of their loss. The higher-level
protocols that use IP must implement their own reliability procedures if
reliable communication is required.
For information about IPv6 and ICMP, refer to Cisco IOS IPv6 Configuration Guide, Release 12.4 and Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference, Release 12.4.
Type 3 Destination Unreachable Error Messages
Type 3 error messages are sent when a message
cannot be delivered completely to the application at a destination host.
Six codes contained in the ICMP header describe the unreachable
condition as follows:
• 0—Network unreachable
0—Network unreachable
• 1—Host unreachable
1—Host unreachable
• 2—Protocol unreachable
2—Protocol unreachable
• 3—Port unreachable
3—Port unreachable
• 4—Fragmentation needed and Don't Fragment (DF) bit set
4—Fragmentation needed and Don't Fragment (DF) bit set
• 5—Source route failed
5—Source route failed
Cisco IOS software can suppress the generation
of ICMP unreachable destination error messages, which is called
rate-limiting. The default is no unreachable messages more often than
once every half second. Separate intervals can be configured for code 4
and all other unreachable destination error messages. However, there is
no method of displaying how many ICMP messages have not been sent.
The ICMP Unreachable Destination Counters
feature provides a method to count and display the unsent Type 3
messages. This feature also provides console logging with error messages
when there are periods of excessive rate limiting that would indicate a
Denial of Service (DoS) attack against the router.
Denial of Service Attack
A DoS attack occurs when a stream of ICMP echo
requests (pings) are broadcast to a destination subnet. The source
addresses of these requests are falsified to be the source address of
the target. For each request sent by the attacker, many hosts on the
subnet will respond flooding the target and wasting bandwidth. The most
common DoS attack is called a "smurf" attack, named after an executable
program and is in the category of network-level attacks against hosts.
DoS attacks can be easily detected when error-message logging of the
ICMP Unreachable Destination Counters feature is enabled.
How to Configure ICMP Unreachable Destination Counters
This section contains the following procedures:
Clearing the ICMP Unreachable Destination Packet Statistics
Perform this task to clear all of the
unreachable destination packet statistics. This task is beneficial to
begin a new log after the thresholds have been set.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.  enable
enable
2.  clear ip icmp rate-limit [interface-type interface-number]
clear ip icmp rate-limit [interface-type interface-number]
3.  end
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring ICMP Unreachable Destination Counters and Logging Intervals
Perform this task to specify an interval number
for unreachable destination messages and a packet counter (threshold)
and interval to trigger a logging message to a console. Counting begins
as soon as this command is configured.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.  enable
enable
2.  configure terminal
configure terminal
3.  ip icmp rate-limit unreachable [df] [ms] [log [packets] [interval-ms]]
ip icmp rate-limit unreachable [df] [ms] [log [packets] [interval-ms]]
4.  exit
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Displaying the ICMP Unreachable Destination Packets
Perform this optional task to display all of
the unreachable destination packet statistics, which include dropped
packets. Counting begins as soon as ip icmp rate-limit unreachable command is configured.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.  enable
enable
2.  show ip icmp rate-limit [interface-type interface-number]
show ip icmp rate-limit [interface-type interface-number]
3.  end
end
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following output using the show ip icmp rate-limit command displays the unreachable destinations by interface:
Router# show ip icmp rate-limit
DF bit unreachables All other unreachables
Interval (millisecond) 500 500
Interface # DF bit unreachables # All other unreachables
--------- --------------------- ------------------------
Ethernet0/0 0 0
Ethernet0/2 0 0
Serial3/0/3 0 19
The greatest number of unreachables is on serial interface 3/0/3.
Configuration Examples for ICMP Unreachable Packet Counters
This section provides the following configuration example:
ICMP Rate-Limit Unreachable Log Configuration: Example
In the following example, console logging begins with a packet threshold of 1200 and every 120,000 ms:
ip icmp rate-limit unreachable log 1200 120000
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to ICMP Unreachable Destination Counters feature.
Related Documents
Standards
|
Standards
|
Title
|
|---|---|
No new or
modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for
existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
|
—
|
MIBs
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents new and modified commands only.
New Commands
Modified Commands
clear ip icmp rate-limit
To clear all Internet Control Message Protocol
(ICMP) unreachable rate-limiting statistics or all statistics for a
specified interface, use the clear ip icmp rate-limit command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear ip icmp rate-limit [interface-type interface-number]
Syntax Description
Defaults
All unreachable statistics for all devices are cleared.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following example shows how to clear all unreachable statistics on all interfaces:
Router# clear icmp rate-limit
Related Commands
ip icmp rate-limit unreachable
To limit the rate at which Internet Control
Message Protocol (ICMP) unreachable messages are generated for a
destination, use the ip icmp rate-limit unreachable command in global configuration mode. To use the default, use the no form of this command.
ip icmp rate-limit unreachable [df] [ms] [log [packets] [interval-ms]]
no ip icmp rate-limit unreachable [df] [ms] [log [packets] [interval-ms]]
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default value is one ICMP destination unreachable message per 500 ms.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
|
Release
|
Modification
|
|---|---|
12.0
|
This command was introduced.
|
12.4(2)T
|
The packets and the interval-ms arguments and log keyword were introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Counting of packets begins when the command is configured and a packet threshold is specified.
The no ip icmp rate-limit unreachable command turns off the previously configured rate limit. To reset the rate limit to its default value, use the ip icmp rate-limit unreachable command default.
Cisco IOS software maintains two timers: one
for general destination unreachable messages and one for DF destination
unreachable messages. Both share the same time limits and defaults. If
the df option is not configured, the ip icmp rate-limit unreachable command sets the time values in ms for DF destination unreachable messages.
Examples
The following example sets the rate of the ICMP destination unreachable message to one message every 10 ms:
ip icmp rate-limit unreachable 10
The following example turns off the previously configured rate limit:
no ip icmp rate-limit unreachable
The following example sets the rate limit back to the default:
no ip icmp rate-limit unreachable
The following example sets a logging packet threshold and time interval:
ip icmp rate-limit unreachable log 1200 120000
Related Commands
show ip icmp rate-limit
To display all Internet Control Message
Protocol (ICMP) unreachable destination messages or unreachable
destination messages for a specified interface including the number of
dropped packets, use the show ip icmp rate-limit command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip icmp rate-limit [interface-type interface-number]
Syntax Description
Defaults
All unreachable statistics for all devices are displayed.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output when the show ip icmp rate-limit command is entered and unreachable messages are generated:
Router# show ip icmp rate-limit
DF bit unreachables All other unreachables
Interval (millisecond) 500 500
Interface # DF bit unreachables # All other unreachables
--------- --------------------- ------------------------
Ethernet0/0 0 0
Ethernet0/2 0 0
Serial3/0/3 0 19
The greatest number of unreachables on Serial3/0/3 is 19.
The following is sample output when the show ip icmp rate-limit command is entered and the rate-limit interval has been set at 500. The packet threshold has been set at 1 by using the ip icmp rate-limit unreachable
command, so the logging will display on the console when the threshold
is exceeded. The total suppressed packets since last log message is
displayed.
Router# show ip icmp rate-limit
00:04:18: %IP-3-ICMPRATELIMIT: 2 unreachables rate-limited within 60000 milliseconds on Serial3/0/3. 17 log messages suppressed since last log message displayed on Serial3/0/3
Table 1 describes the significant fields shown in the display.
-================================
How ICMP Redirect Messages Work
ICMP redirect messages are used by routers to notify the hosts on the data link that a better route is available for a particular destination.For example, the two routers R1 and R2 are connected to the same Ethernet segment as Host H. The default gateway for Host H is configured to use router R1. Host H sends a packet to router R1 to reach the destination on Remote Branch office Host 10.1.1.1. Router R1, after it consults its routing table, finds that the next-hop to reach Host 10.1.1.1 is router R2. Now router R1 must forward the packet out the same Ethernet interface on which it was received. Router R1 forwards the packet to router R2 and also sends an ICMP redirect message to Host H. This informs the host that the best route to reach Host 10.1.1.1 is by way of router R2. Host H then forwards all the subsequent packets destined for Host 10.1.1.1 to router R2.
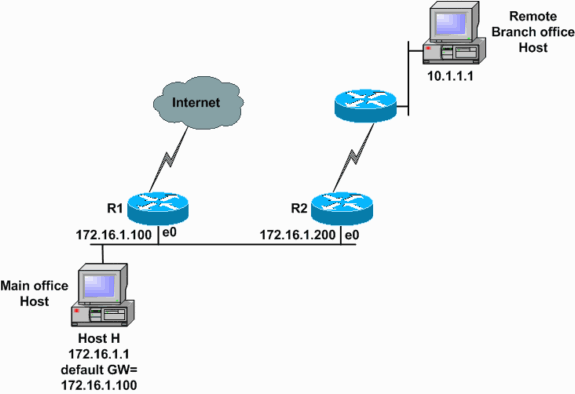
This debug message shows router R1, as in the network diagram, sending an ICMP redirect message to Host H (172.16.1.1).
Router R1 (172.16.1.100) sends a redirect to Host H (172.16.1.1) to use router R2 (172.16.1.200) as the gateway to reach the destination 10.1.1.1.R1# debug ip icmp ICMP packet debugging is on *Mar 18 06:28:54: ICMP:redirect sent to 172.16.1.1 for dest 10.1.1.1, use gw 172.16.1.200 R1#
When Are ICMP Redirects Sent?
Cisco routers send ICMP redirects when all of these conditions are met:-
The interface on which the packet comes into the router is the same
interface on which the packet gets routed out.
-
The subnet or network of the source IP address is on the same subnet
or network of the next-hop IP address of the routed packet.
-
The datagram is not source-routed.
-
The kernel is configured to send redirects. (By default, Cisco
routers send ICMP redirects. The interface subcommand
no ip
redirects
can be used to disable ICMP redirects.)
For example, if a router has two IP addresses on one of its interfaces:
If the router receives a packet that is sourced from a host in the subnet 171.68.179.0 and destined to a host in the subnet 171.68.254.0, the router does not send an ICMP redirect because only the first condition is met, not the second.interface ethernet 0 ip address 171.68.179.1 255.255.255.0 ip address 171.68.254.1 255.255.255.0 secondary
The original packet for which the router sends a redirect still gets routed to the correct destination.